The spinal column consists of twenty-three vertebral discs.
They are found between each vertebra and are also known as intervertebral discs.
They have the function of providing the spine with flexibility, assist the body during movement and serve as shock absorbers, one of their main functions.
This helps prevent straining of the spine and protects the nerves, the brain and other near-found structures. They are made out of a material that is fibrocartilaginous, a combination of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue.
The outer area of the disks is called the annulus fibrosis. The inner area of the disks is a mucoprotein gel, which moves and absorbs pressure. It affects the spine less by redistributing itself and absorbing the pressure put on the spine. (1)
What´s a herniated disk?
As we age, the pressure the disk absorbs starts affecting the gel itself and it ends up absorbing less and less pressure and putting more and more shock on the spine.
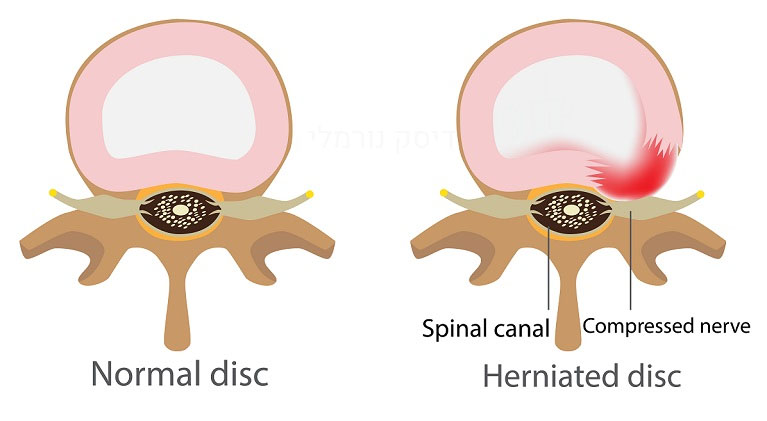
The outer part gets affected as well and may start to rip, causing severe back pain. This is what´s other known as a herniated disk. (2)
There are 31 pairs of nerves that may be affected by a disc hernia and all leave different parts of the spine and are divided after this feature into 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal.
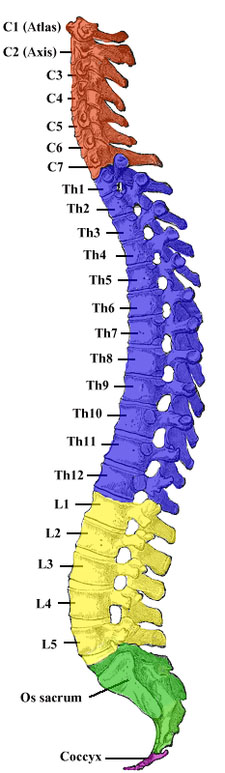 Parallelly, there are 7 cervical discs (C1-C7), 12 thoracic disks (T1-T12), 5 lumbar discs (L1 to L5), 5 sacral discs (S1 to S5). The end of the spinal cord, the coccyges, is made out of four small bones. The area between L5 and S1 is most prone to develop a rupture of the disc and cause chronic back pain.
Parallelly, there are 7 cervical discs (C1-C7), 12 thoracic disks (T1-T12), 5 lumbar discs (L1 to L5), 5 sacral discs (S1 to S5). The end of the spinal cord, the coccyges, is made out of four small bones. The area between L5 and S1 is most prone to develop a rupture of the disc and cause chronic back pain.
Depending the affected area, they are divided into:
Intradural disc herniation- an extremely rare condition and is caused when the inner part of the disc is dislocated into the Dural sac, the outermost layer of the meninges, the membranes that cover the spinal cord (3).
Cervical disc herniation- named after the cervical vertebrae, the vertebrae of the neck, C1 to C7. A cervical disc herniation usually occurs between C5 and C6 or between C6 and C7. Pain in the neck, shoulders and arms are symptoms common specifically for a cervical disc herniation.
Lumbar disc herniation– as the name shows, occur between the vertebrae L4 and L5 or L5 and the sacrum. Lower back pain, pain in the foot or toes are indicators of a lumbar disc herniation.
What are the major symptoms of a herniated disk?
There are cases, in which there is a rupture in the disk and person is not even aware of it. With time, however, symptoms start to show.
These are most commonly described as sharp back pain, a cramping and tightness of the muscles, pain that reaches up to the shoulders and down on the legs, neck pain, headaches or a tingling feeling in the arms or legs.
If any back pain is combined with a tingling sensation, a weakness or numbness, it is most recommended to consult a doctor.
What are the major causes of a herniated disk?
The main cause for a herniated disk is the condition, in which the gel in the inner are of the disc starts to absorb less shock, allowing the spine to move more and receive more pressure. Therefore, it is more than possible that these weakened discs start to rip.
Massive pressure, such as after an accident or a heavy injury, are also factors that may increase the chance of having a herniated disc.
The pressure after such an injury is too much to bear for the discs, so that they rip and allow the spine to have to bear more pressure than it can.
Doctors very often advise to be careful when lifting heavy objects and make sure to lift properly, putting less pressure on your spine. The rupture happens the same way as after an injury, the pressure of the heavy objects is too much for the disks to bear.
The same pressure can be put upon the spine by being obese and a healthy weight is, amongst others, important for the spine as well.
Smoking is another risk factor of herniated disks, which patients can control and help preventing the condition by quitting smoking.
A risk factor one cannot prevent is the genetic predisposition, which also has an influence on the discs ability to absorb shock. It is known that in some cases, having a family member with a herniated disc, increases the chances of having to deal with the condition yourself.
What treatment options are there?
The first treatment to consider is the non-invasive therapy, in which different types of exercises and positions are repeated, to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles.(4)
The additional strength helps support the back more, putting less pressure on the ruptured disc and decreasing inflammation.
Placing hot or cool elements on the painful area may also result to be helpful in decreasing pain and inflammation.
There are also braces that can be used, to better the position of your pack, decreasing muscle tensions, strengthening the muscles and hereby providing more support to your spine.
Medication may also be used to help against the pain. Most commonly, anti-inflammatory drugs or oral steroids are prescribed. This is however not recommended and should only be used in cases of severe pain.
As discomfort is usually felt often throughout the day, some patients may begin to use more painkillers than recommended, leading herewith to damaging consequences.
There are also epidural injections that can be done on the affected area, to relax the muscles and ease the pain. (5)
Epidural is the area within the spinal canal, in which spinal nerve roots are found, as well as fat, tissue and blood vessels.
The epidural injection injects therapeutic, pain-relieving substance into this area, preventing the nerve roots from transmitting pain to the brain. Most epidural injections are corticosteroid, sometimes in combination with a local anesthetic and sometimes without it.
In mild cases, a local anesthetic without corticosteroid is enough helpful to ease the pain. A combination of all above mentioned methods should be tried out to find what best works for each individual.
The goal is to decrease the discomfort and pressure on the spine in a non-invasive way.
There are also some natural remedies that are considered to help patients and are worth trying.
- White willow is a plant known to have similar effects on the body as aspirin. It has anti-inflammatory features and is therefore good for treating the inflammation of the disc as well as the back pain caused by it.
- Cayenne pepper is another natural remedy. It should be used as a “hot therapy” and applied to the aching area of the back. There are many creams that contain cayenne pepper and can be found at the drug store.
- Turmeric is a spice many use while cooking and those who don´t and have been diagnosed with herniated disk should start using more. Turmeric is known to be pain relieving and improves circulation, which automatically eases the muscle pain in the affected area.
- Colchicine is a plant from which aspirin is made. Using the plant directly is a good alternative to pain medication and has been proved to help with pain management.
If the non-invasive treatment options show to be helpless, invasive therapy might have to be considered. Usually, the non-invasive therapy is applied for a period of four to six weeks. There are some invasive procedures, that are minimal, require only a small incision and have a shorter healing time. Therefore, traumatize the body less and are the next best step to try. Some of these procedures are:
Discectomies, a procedure in with the herniated part of the disk is removed, hereby putting less pressure on the area that surrounded it. After removing the herniated part, the ruptured wall of the disc is treated to minimize the possibility of a further rupture.
A microdiscectomy is very similar to the discectomy. The difference is in the way the procedure is done. In a microdiscectomy the inner herniated area is reached through the upper region of the spine.
Another procedure consists of removing the ruptured part and placing a so-called bridge, made out of bone between the two vertebrae, instead of the disc.
This used material leads to the two vertebrae attaching to one another, forming one whole vertebrae. At the end of the healing period, there is less pressure and discomfort on the nerves that surrounded the herniated disk. This procedure is known as fusion.
How is it diagnosed?
There are some common indicators that help the physicians diagnose a herniated disk.
Symptoms, such as what type of pain is present, in which pain and at what time can be the first step to the right diagnosis.
Health condition is also important to determine, as if you´re already dealing with a bone-related condition, such as osteoporosis, it may increase your chances of disk hernia.
Your family health condition as well as any accidents or injuries are also important to share with your physician. Usually, your neurological condition will be tested first to exclude any abnormalities within your nerve system.
LaSegue test is another test that can be immediately perform during a physical exam and is a good indicator for the condition.
During this test, the patient needs to stretch he leg, while lying on the back. If the patients feel pain at a degree of thirty to seventy, it is acknowledged as a sign of a herniated disc.
These stretches are performed to find out which motion causes the pain, hereby located the right affected area.
Fever is a known sign of an infection, while an increased pulse rate or blood pressure are indicators of pain.
After the physical exam, in some cases but not all, imaging tests may be done to confirm the diagnose and exclude conditions that may show similar symptoms, such as a tumor, fracture or infection.
Imaging tests that may be used are:
- MRI – shows best which disk is herniated, where it is located and which nerves are affected by it.
- CT – is an alternative to MRI, that is used in cases where MRI can´t be implemented, for example if the patient is claustrophobic or obese.
- X-Ray– does not diagnose a herniated disc but may be used during examination to exclude a broken bone, a tumor or an infection.
- EMG– helps show the affected nerves.
- CT myelogram- uses a contrast fluid which is injected in the spinal fluid and shows where the disc is located and what size it has. A CT myelogram is not a common exam, as it´s very invasive and physicians try to avoid it.
Can a herniated disk be prevented?
There are some risk factors for herniated disc that are easily controllable and patients should consider, before getting the diagnose and especially after it.
Try to watch out your posture, if you smoke start quitting immediately, maintain a healthy weight, exercise the proper way and only practice sports that put less pressure on the spine, such as swimming.
Yoga is another way of stretching your body and performing exercises that strengthen your back muscles. Surely, some risk factors are uncontrollable, such as the normal process of less shock absorption of the spine disc, caused by age.
A herniated disk may lead to complications. At the lower part of the spinal cord, long nerve roots are formed, which are known as cauda equina. (6)
In some cases of disk herniation, all these nerve roots are compressed, leading to permanent weakness and in some rare cases even paralysis. Other consequences may be a bowel or bladder dysfunction, with incontinency as a main symptom and difficulties urinating, even when the bladder is full. The pain may become so severe, that the patient is no longer able to go on with their usual daily activities.
Emergency surgery may be necessary in cases of sudden paralysis or numbness.
Refrences:
- 1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6229/
- 2) Dandy WE. Serious complications of ruptured intervertebral disks. JAMA. 1942;119:474–477. doi: 10.1001/jama.1942.02830230008002
- 3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK410166/
- 4) https://www.healthline.com/health/fitness-exercise/herniated-disk-exercises
- 5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3641279/
- 6) https://www.medicinenet.com/herniated_disc/article.htm#herniated_disc_facts

